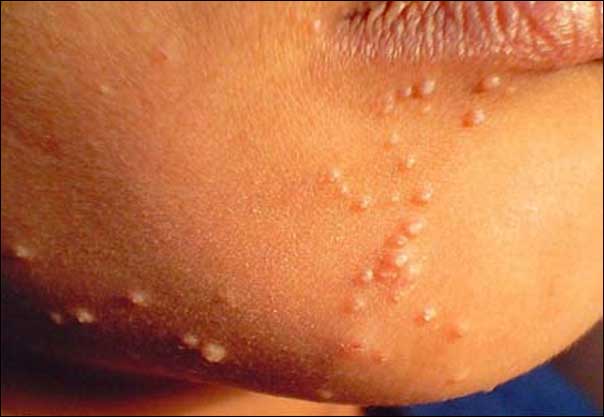
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection caused by a virus. It’s characterized by small, raised bumps on the skin that may be pink, white, or flesh-colored. They often have an indentation in the middle and are usually painless. While molluscum contagiosum can affect anyone, it’s most common in children ages 1 to 10. The virus that causes molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or object, such as towels or toys. It can also spread through sexual contact. In some cases, it may even spread from one area of your own body to another. Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum include small bumps that can range in size from very tiny to about the size of a pencil eraser.
The bumps may be flesh-colored, pink, white, or red and often have a dimple in the center. They may be itchy or sore but are usually painless. In some cases, they may also become inflamed or filled with pus. Molluscum contagiosum is usually diagnosed based on its appearance but your doctor may take a sample for testing if needed to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment isn’t always necessary as the infection will typically go away on its own without any intervention within 6 to 12 months. However, treatment options are available if you want to speed up the process or reduce symptoms such as itching and inflammation.
What Causes Molluscum Contagiosum and How Can You Treat It?
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin condition caused by a virus. It’s contagious, meaning it can spread from person to person through close contact. The virus usually affects children, though it can affect adults as well. It’s characterized by small bumps on the skin that are typically painless and can range in color from pink to white.
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus known as molluscipoxvirus. This virus is highly contagious and spreads through close contact with someone who has it or with objects they have touched, such as towels or clothing. It can also spread through sexual contact, although this is less common. The virus thrives in warm, moist environments like swimming pools or gym locker rooms, which makes it more likely to spread from person to person.
The condition is most common in children because their immune systems are still developing and may not be able to fight off the virus as easily as an adult’s immune system can. In rare cases, molluscum contagiosum can be caused by other types of viruses such as herpes simplex virus (HSV) or human papillomavirus (HPV). These cases are usually seen in adults who have weakened immune systems due to certain medical conditions or treatments.
Treatment Options for Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection caused by a virus, and it can affect people of all ages. It is a common infection that causes small bumps to form on the skin, which can be itchy and uncomfortable. Treatment options for molluscum contagiosum depend on the severity of the condition and the patient’s age. In most cases, molluscum contagiosum will resolve itself without treatment, usually within 6-12 months.
However, if you are concerned about the appearance or discomfort caused by the infection, there are several treatments available that can help reduce symptoms and speed up recovery. One of the most common treatments for molluscum contagiosum is cryotherapy. This involves freezing the bumps with liquid nitrogen in order to destroy them. This is an effective treatment but may cause some temporary discomfort or pain. Another treatment option is topical creams or ointments that contain antiviral ingredients such as podophyllotoxin or imiquimod.
These creams can help to reduce symptoms and speed up recovery time. However, they may cause side effects such as burning, itching, redness and swelling at the site of application. In some cases, laser therapy may be used to treat molluscum contagiosum. This involves using a laser beam to destroy the virus that causes the infection. Laser therapy is an effective treatment but may cause some temporary discomfort or pain at the site of application. If you have molluscum contagiosum, it is important to speak to your doctor about which treatment option is best for you so that you can get back to feeling your best as soon as possible!
Prevention Strategies to Avoid Getting Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection caused by a virus. It is contagious and it can spread through direct contact or through contaminated objects. Even though molluscum contagiosum is generally harmless, it can be quite uncomfortable and unsightly. To prevent molluscum contagiosum, there are several strategies you can take:
- Wash your hands often with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, and clothing.
- Cover any affected areas with clothing or bandages.
- Clean any surfaces that may have come into contact with the virus.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the bumps.
These prevention strategies can help reduce your risk of getting molluscum contagiosum. However, if you think you may already have the virus, talk to your doctor about the best treatment options for you.
Conclusion: Summary of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a common, mild skin infection that is caused by a virus. It often affects children and can be spread through direct contact with the infected area, or indirectly from contaminated items. Symptoms include small, raised bumps on the skin that may be itchy or sore. Treatment options include home remedies such as over-the-counter creams and lotions, as well as prescription medications. In most cases, molluscum contagiosum will go away on its own without treatment within several months to a year. However, if symptoms are persistent or bothersome, your doctor may recommend treatment to speed up the healing process.